Clip from Shifty (2025) by Adam Curtis. Alan Budd reflects on the possibility that economic policies presented as technical necessities can also function to weaken labour, reshape class power, and restore profitability. Although grounded in 1980s Britain, the mechanism he describes—crisis, discipline, unemployment—has reappeared many times since, and continues to surface in contemporary economic policy debates.
Another interesting post from Quora, this one on thinking styles and Maduro
Jan. 12th, 2026 03:00 pmQuestion: How many Democrats are pro-Maduro?
Reply: Zero.
Back in my uni days, I took a class in cognitive science that was one of my favorite courses. One of the many, many things we talked about in class was the difference between abstract thinkers and concrete thinkers.
This difference appears to be architectural, a consequence of how your brain is wired, not a matter of choice or education.
Concrete thinkers see the world in strict black and white terms. They have difficulty drawing indirect connections between things, struggle to see multiple perspectives, and tend to hold an all or nothing, with-us-or-against-us mentality.
Abstract thinkers understand complex associations, can understand multiple perspectives at the same time, and can see second and third order relationships between things.
And crucially, abstract thinkers can understand concrete thought patterns, but generally speaking, concrete thinkers seem physically incapable of understanding abstract thought patterns.
So here’s the thing:
Abstract thinkers are capable of grasping multiple ideas at once. Like, “Maduro is an illegitimate totalitarian ruler with an authoritarian bent who presided over an illegitimate government” and also “a unilateral move to depose Maduro is illegal under international treaties and morally wrong.”
Concrete thinkers be all like “you’re either good or your bad, and if you’re bad you deserve anything bad that happens to you, anyone who says Maduro shouldn’t have been kidnapped must live and support Maduro.”
Abstract thinkers be like “no, you can believe a person is bad and also believe that breaking the law to kidnap that person is bad too, both of those things can be true at the same time.”
Very interesting, I wish we had classes available here on such a topic. I'm not sure how much I agree with it being a structural thing vs an education thing, I'd want to see some information on that, I'd be open to discussion.
I can certainly see where some conservative people whom I know/knew had problems with abstract thinking. I think I would hazard to say that concrete thinkers might be more easily persuaded by ideologues since they would be more likely to present their arguments and ideas in more concrete 'for or against' terms with straw man arguments that appear harder to refute.
Personally I've never had problems to easily see and argue multiple sides of an argument. When I first started working here at the university, around 20 years ago in the computer lab, we had one guy who had a degree in philosophy, and we had a security guard who was an ex-cop and a former preacher, and another who just liked discussing things in a lively fashion. And we had these informal round tables where we'd argue the issues of the day, going around and round, picking up and discarding different viewpoints. It was tremendous fun. But it only lasted about a year before I left and the group broke apart.
I know I definitely prefer to associate more with abstract thinkers, they're much more fun to talk and argue (more in a discuss way, not combative ) things with.
Title: Caryatid.
Author:
Fandom: Wake Up Dead Man (2025)
Series: Part 2 of Pillar Of The Community
Rating: G
Archives: Archive Of Our Own, SquidgeWorld
Summary: "How did you know?" Jud asks Blanc.
( Coda )
After spending large parts of December getting behind and catching up and getting behind and catching up... I finished Zevachim two days early. The power of bamos! ;) On to Menachos!
My notes behind cut.
We're also about a year and a half out from the end of this cycle, which means I have already gotten one gentle "hey, do you know where you'll be on June 7, 2027"-type email from an org. No, I do not think this is too early, actually. Gotta make plans. Deeply hoping I can avoid being involved in organizing the in person thing here, but I have a suspicion that if I'm not involved, it may end up as unwelcoming as the women's siyum hashas I went to at the end of the last cycle. (I do trust a couple of the people likely to attend it, but I don't know who is going to be organizing anything here. So I may need to try to get involved against my will.) It wasn't actually that bad overall -- aside from how it's still, y'know, memorable 6 years removed from it -- but I am quite frankly more willing to get into an airplane and fly to a different city than go through that again. (okay more realistically if it ends up organized by a group I do not trust at all, I'd zoom in to a larger event and be done with it)
( Read more... )
This really shouldn't be the case but as far as I can tell, I am in at least the top 5% (maybe even considerably smaller than that) of people regarding knowledge of what went on during the production of The Last House on the Left. I have achieved this not through formal expertise or through special access, but by merely:
1) Going through the DVD/Blu-ray extras systematically
2) Reading all of David Szulkin's making-of book
3) Spending more than three minutes searching for evidence
Given Last House was the film that launched Wes Craven's career in horror, it is absolutely absurd how useless the horror and cinema media have been, for decades, in interrogating what happened away from the fictional story. Wes Craven himself should have been asked far more searching questions than he was.
This criticism applies to cinema academics too. It's deeply ironic, in a bad way, that there have been so many people writing papers and articles about the way Mari is portrayed in the story from various progressive and feminist viewpoints, yet almost none writing about the serious abuse by men of the real young woman who played Mari.
The fact that the most likely place to find details of what Sandra Peabody endured is in listicles is a terrible indictment of how badly so-called "serious" horror and cinema media have failed.
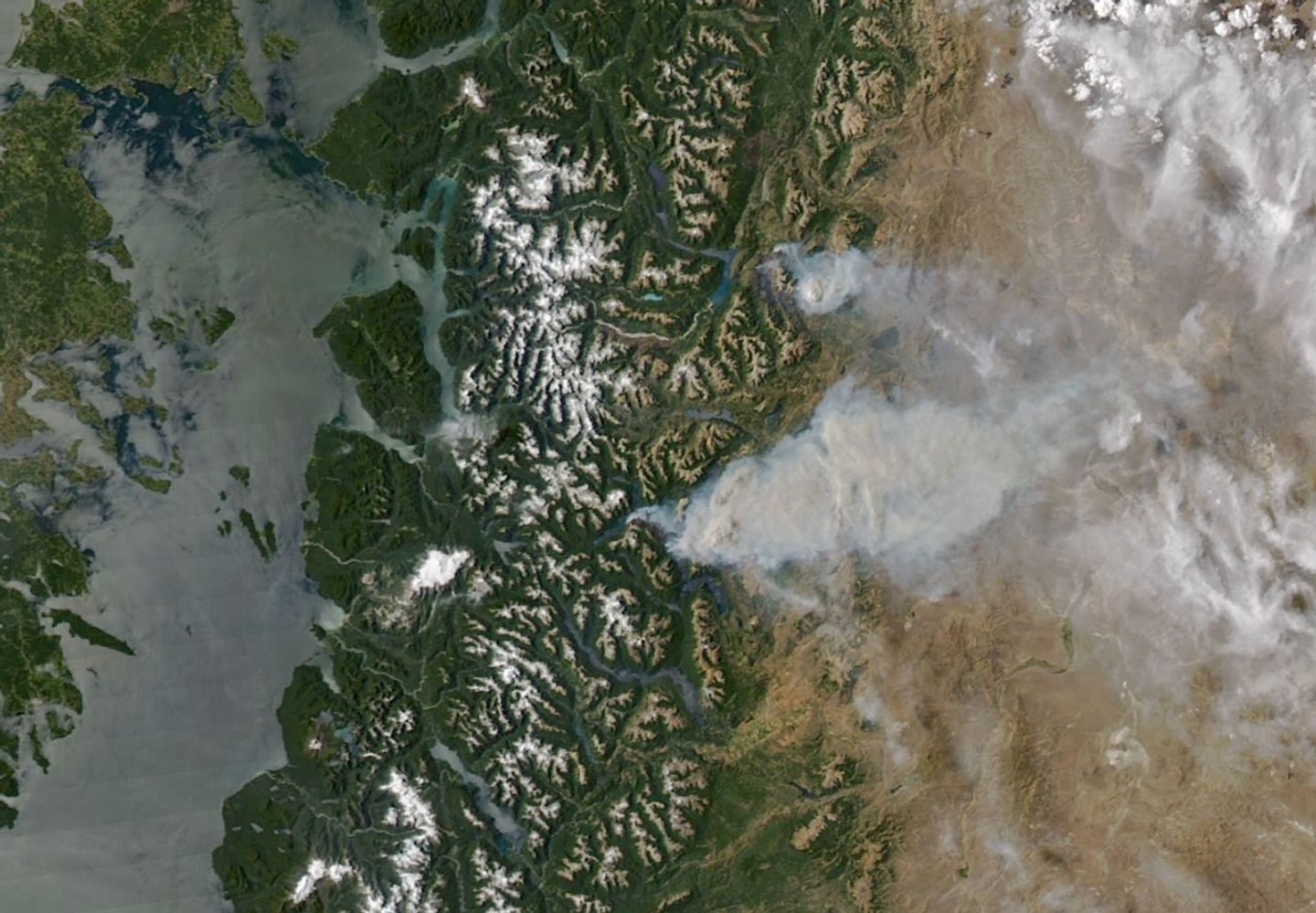
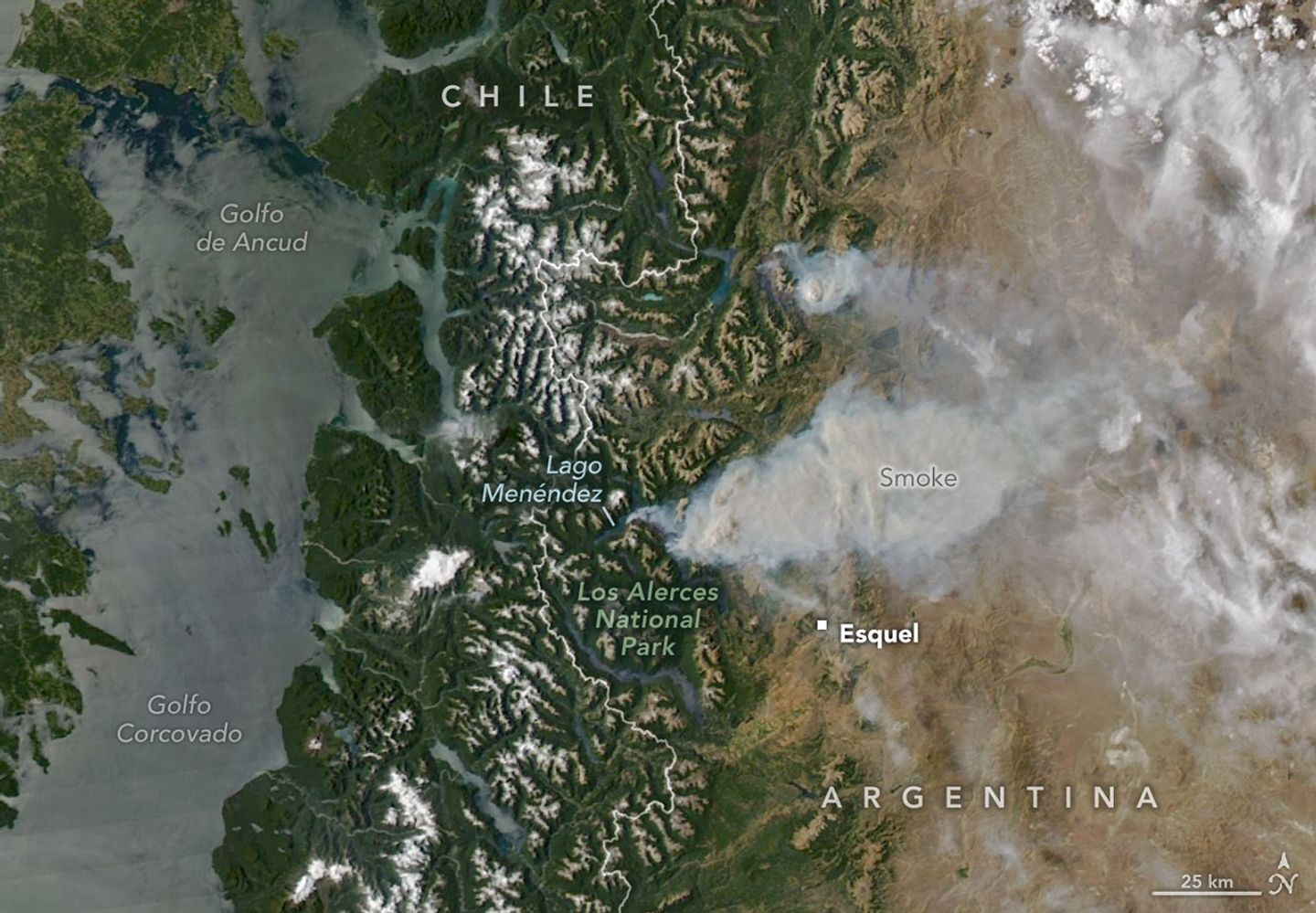
Summer is usually peak tourism season in Argentina’s Chubut province, a time when hikers and sightseers arrive to explore glacial lakes and cirques, alpine valleys, and towering forests. In January 2026, however, some visitors to the remote Patagonian region instead found themselves fleeing raging wildland fires.
On January 8, 2026, the MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) on NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this image of smoke billowing from two large fires burning in and around Los Alerces National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage site. NASA satellites began detecting widespread fire activity in the area on January 6.
The more southerly blaze was spreading east on ridges between Lago Rivadavia, Lago Futalaufquen, and Lago Menéndez; the more northerly fire was burning on steep hillsides around Lago Epuyén. All of the lakes occupy U-shaped glacial troughs, valleys with unusually flat bases and steep sides carved by glacial and periglacial erosion. Satellite-based estimates from the Global Wildfire Information System indicate that fires charred more than 175 square kilometers (67 square miles) across Patagonia between January 5 and 8.
The ridges are blanketed with temperate Patagonian Andean forest, including sections of Valdivian rainforest, with rare stands of alerce (Fitzroya cupressoides). A type of cypress, these huge, slow-growing conifers are the second-longest-lived trees on Earth, with some surviving for more than 3,600 years. According to UNESCO documents, Los Alerces National Park protects 36 percent of Argentina’s alerce forests, including stands with the greatest genetic variability on the eastern slopes of the Andes. The park’s forests also contain exclusive genetic variants and the oldest individuals in the country.
News outlets and the national park reported challenging weather conditions for firefighters on the ground, who faced high temperatures, low humidity, and strong winds in recent days. Standardized Precipitation Index data from the National Integrated Drought Information System show that unusually dry conditions over the past several months have likely primed vegetation to burn. News outlets reported that at least 3,000 tourists had to be evacuated from a lake resort near Lago Epuyén.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Michala Garrison, using MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE and GIBS/Worldview. Story by Adam Voiland.
References & Resources
- Argentina (2026) Parque Nacional Los Alerces. Accessed January 9, 2026.
- Buenos Aires Herald (2026, January 8) Wildfires in Patagonia: 3,000 tourists evacuated as flames consume Chubut forests. Accessed January 9, 2026.
- El Destape (2026, January 5) “Situación explosiva o extremadamente crítica”: alerta por posibles incendios en casi toda la Argentina en el verano. Accessed January 9, 2026.
- France24 (2026, January 7) 3,000 tourists evacuated as Argentine Patagonia battles wildfires. Accessed January 9, 2026.
- LM Neuquén (2026, January 8) Incendios forestales: los lugares habilitados para el turismo en la cordillera. Accessed January 9, 2026.
- NASA Earthdata (2026) Wildfires. Accessed January 9, 2026.
- Noticias Ambientales (2026, January 8) Alert for fires in Chubut: nearly 2000 hectares devastated, 3000 evacuated, and the fire doesn’t stop. Accessed January 9, 2026.
- ReliefWeb (2026, January 8) Argentina – Wildfires. Accessed January 9, 2026.
- UNESCO (2017) Los Alerces National Park. Accessed January 9, 2026.
You may also be interested in:
Stay up-to-date with the latest content from NASA as we explore the universe and discover more about our home planet.

The Bear Gulch fire spread through dense forest and filled skies with smoke in northwestern Washington state.

The fast-growing blaze charred more than 100,000 acres in the span of a week.

Far from large urban areas, Great Basin National Park offers unencumbered views of the night sky and opportunities to study…
The post Fire Threatens Rare Forests in Argentina appeared first on NASA Science.
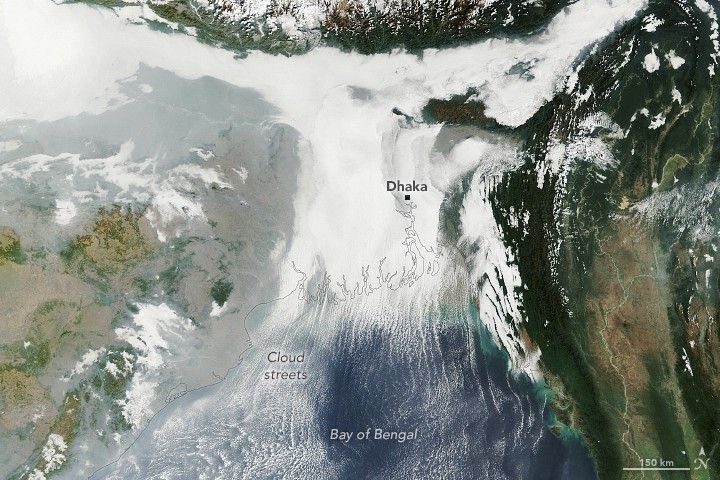
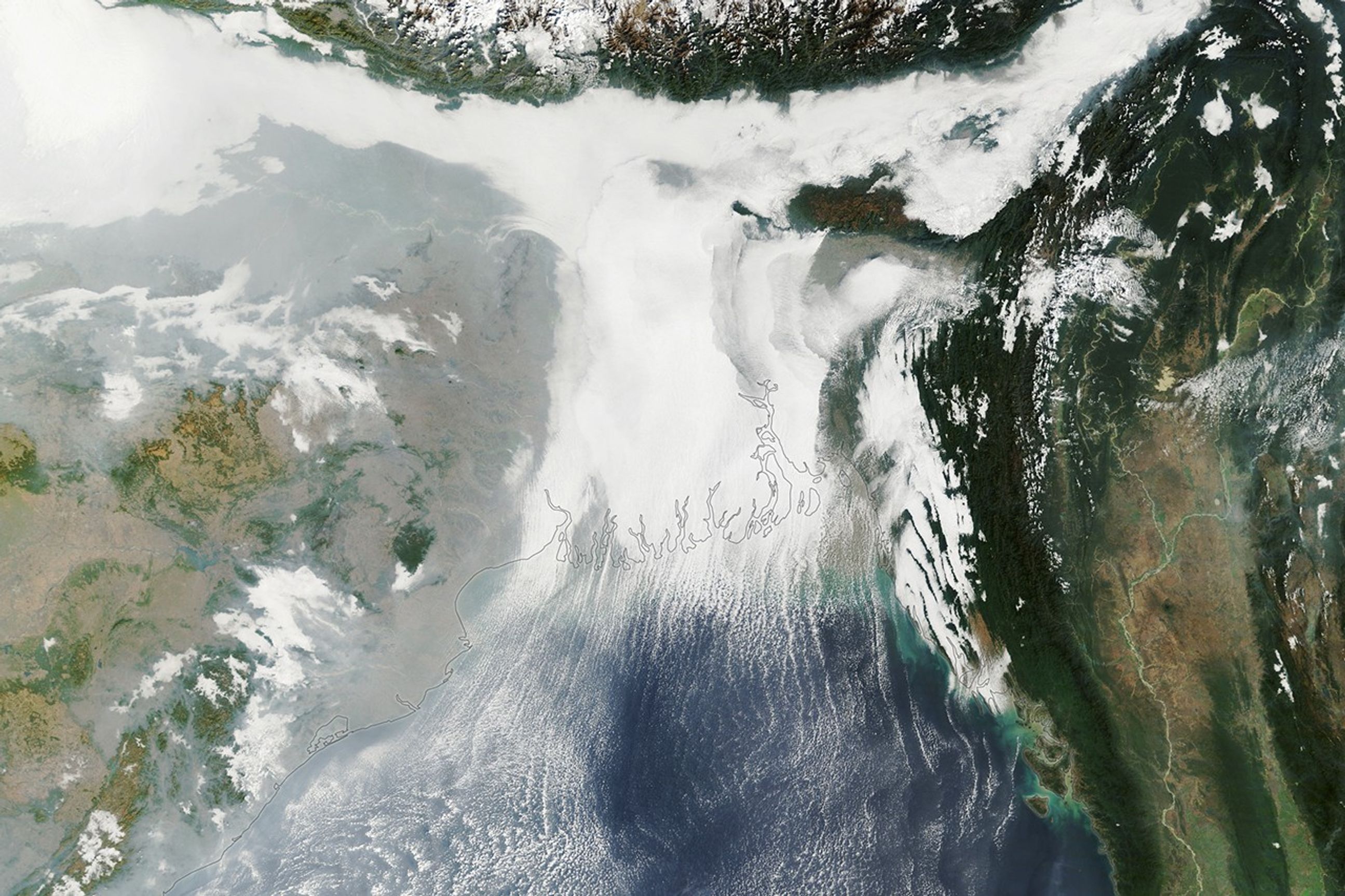
Winter weather took hold across the Indo-Gangetic Plain in early January 2026, bringing dense fog and cold temperatures to much of the flat, fertile lands that span from Pakistan and northern India to Bangladesh.
This image shows low-lying clouds over the delta on the morning of January 6, captured by the MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) on NASA’s Terra satellite. Dense fog, particularly radiation fog, is common this time of year, forming when ground temperatures are cool, winds are light, and moisture is abundant near the surface. The meteorological departments of both Bangladesh and India called for moderate to very dense fog over the region that day amid an ongoing cold wave.
Other relatively low-level clouds extend from the land areas and over the Bay of Bengal. These long, parallel bands of clouds, known as cloud streets, can form when cold air passes over warmer open water, gaining heat and moisture. Rising thermals ascend until they reach a temperature inversion that acts like a lid, forcing the air to roll into long, parallel rotating cylinders. Clouds develop where the air rises, while clear skies appear where the air sinks.
While it appears scenic from above, foggy conditions can pose hazards and snarl daily life for people on the ground. For instance, dense fog early in the month caused major disruptions at the international airport in Dhaka, according to local news reports. Similar disruptions, along with travel delays on roads and railways, were reported in parts of northern, central, and eastern India.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Lauren Dauphin, using MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE and GIBS/Worldview. Story by Kathryn Hansen.
References & Resources
- Bangladesh Meteorological Department (2026, January 5) Weather Forecast Valid For 120 Hours Commencing 06 PM of 05.01.2026. Accessed January 8, 2026.
- Dhaka Tribune (2026, January 2) Flights diverted one after another as dense fog disrupts Dhaka airport operations. Accessed January 8, 2026.
- India Meteorological Department (2026, January 5) Press Release. Accessed January 8, 2026.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2024, January 18) Fog Blankets the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Accessed January 8, 2026.
- The New Indian Express (2026, January 4) Cold wave persist in Delhi, northern India, flights disrupted amid dense fog. Accessed January 8, 2026.
You may also be interested in:
Stay up-to-date with the latest content from NASA as we explore the universe and discover more about our home planet.

The right combination of conditions allowed this distinctive low cloud to form in California’s Central Valley for weeks.

A collection of fish-shaped clouds hovered above the glacial lake in Patagonia in December 2025.

Scientists say the seasonal crop fires are burning later in the day than in previous years.
The post Ganges Delta Under a Winter Shroud of Fog appeared first on NASA Science.
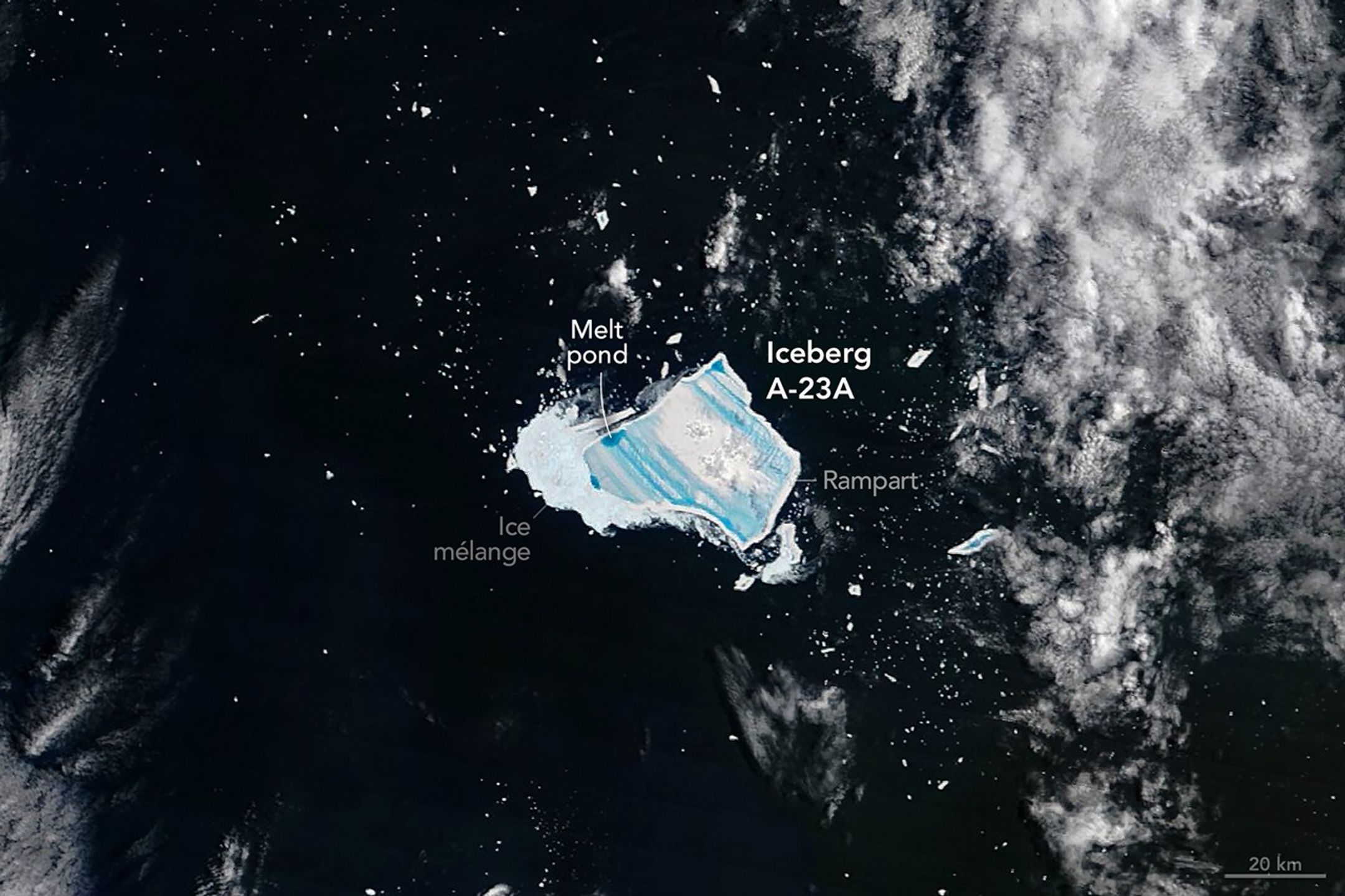
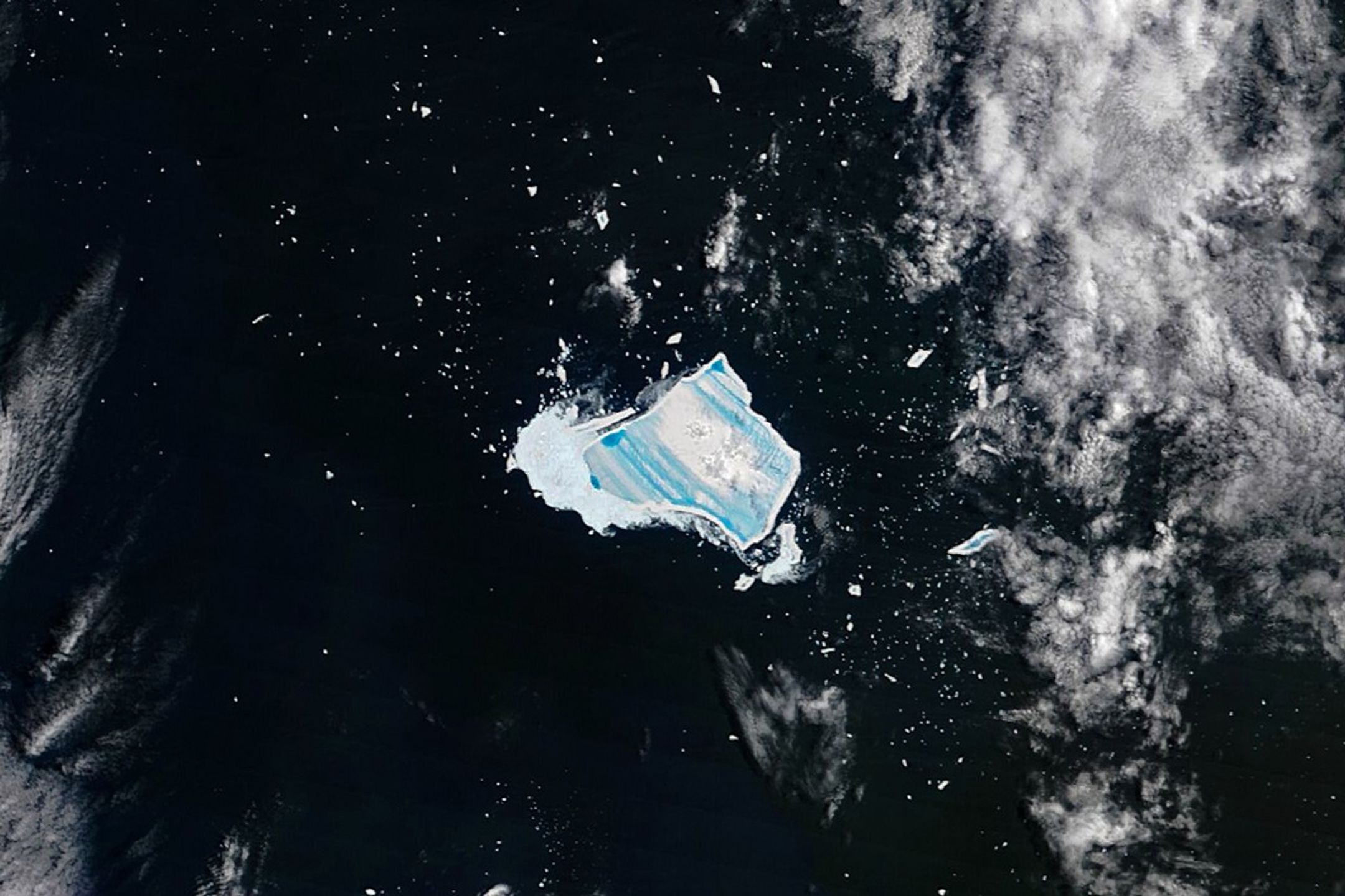
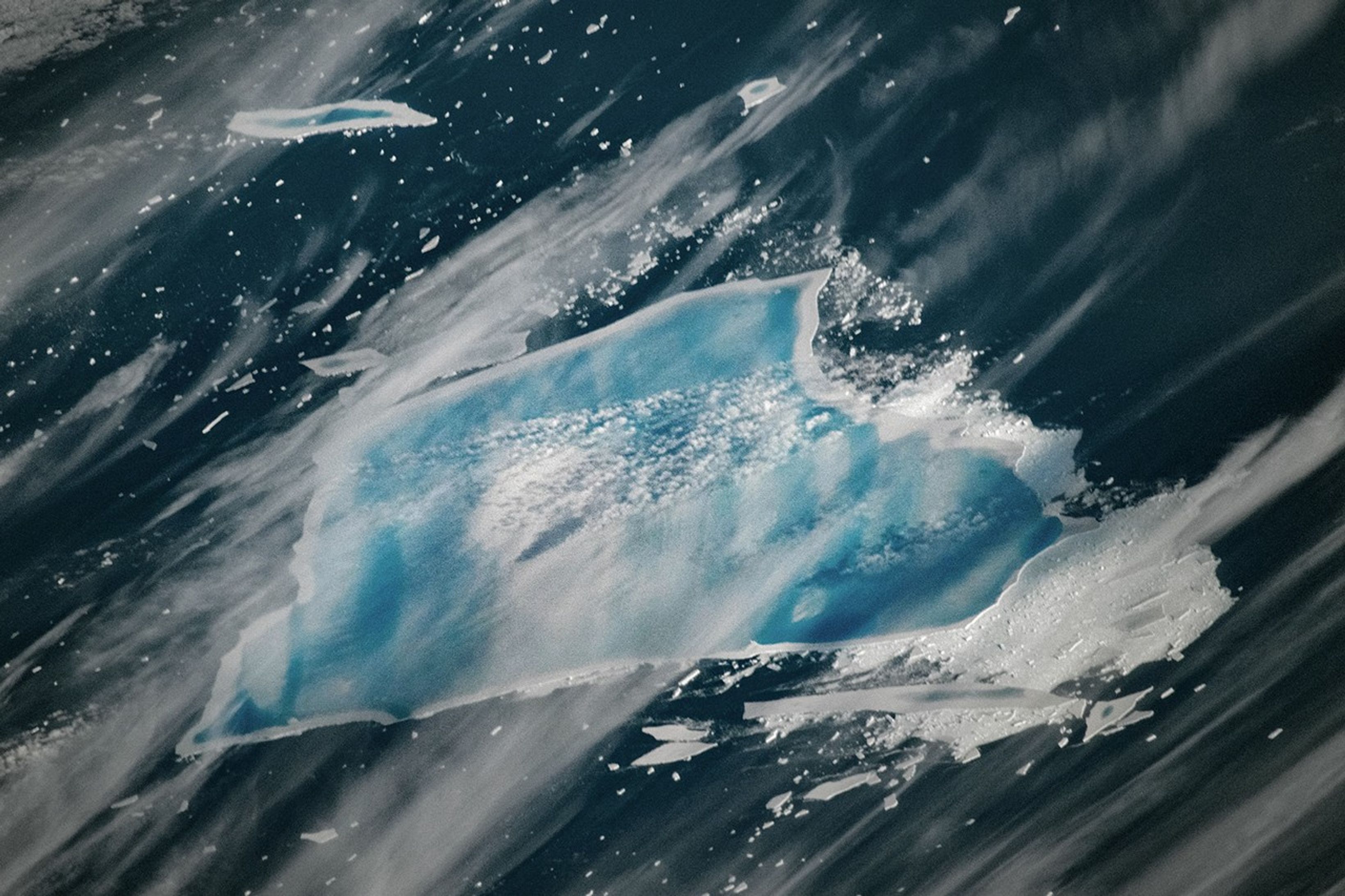
The year that iceberg A-23A first broke away from Antarctica’s Filchner Ice Shelf, Ronald Reagan was president of the United States, and the movie Top Gun was setting box office records. Forty years later, the massive tabular berg—one of the largest and longest-lived bergs ever tracked by scientists—is sopping with blue meltwater and on the verge of complete disintegration as it drifts in the South Atlantic between the eastern tip of South America and South Georgia island.
When it first detached from Antarctica in 1986, the berg was nearly twice the size of Rhode Island—about 4,000 square kilometers. Estimates from the U.S. National Ice Center put the berg’s area at 1,182 square kilometers (456 square miles) in early January 2026, following the breakup of several sizable pieces in July, August, and September of 2025 as it moved into relatively warm summer conditions by December.
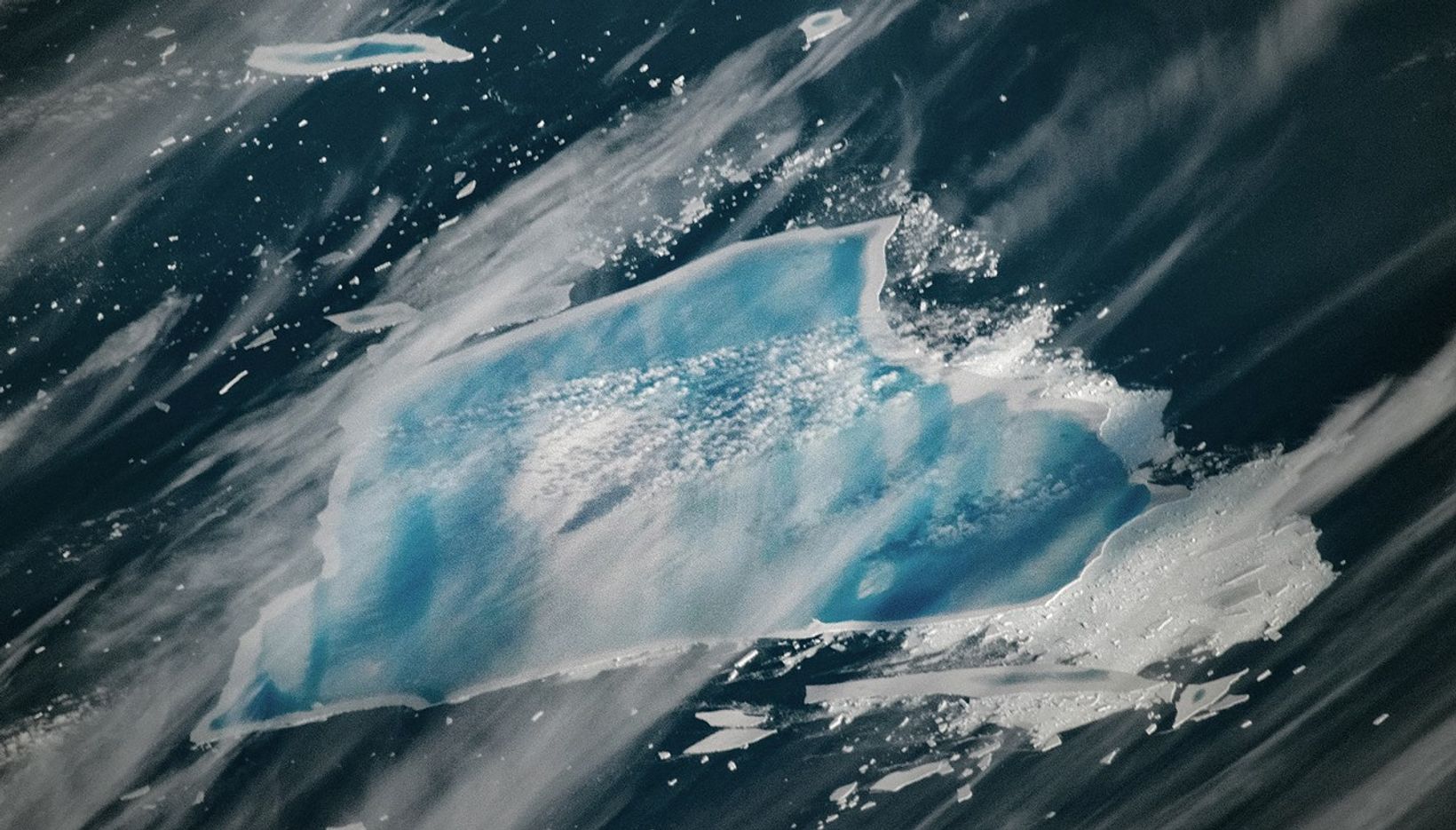
When the MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this image of what remained of the waterlogged berg on December 26, 2025, extensive pools of blue meltwater were visible on its surface. Though much smaller than it once was, what remains is still among the largest icebergs in the ocean, covering an area larger than New York City. An astronaut aboard the International Space Station captured a photograph showing a closer view (below) of the iceberg a day later, with an even more extensive melt pool.
The “blue-mush” areas are likely the result of ongoing disintegration events, explained Ted Scambos, a senior research scientist at the University of Colorado Boulder. “You have the weight of the water sitting inside cracks in the ice and forcing them open,” he said. Note also the thin white line around the outer edge of the iceberg seemingly holding in blue meltwater—a “rampart-moat” pattern caused by an upward bending of the iceberg plate as its edges melt at the waterline.
The striking linear patterns of blue and white across the berg are likely related to striations that were scoured hundreds of years ago when the ice was part of a glacier dragging across Antarctic bedrock.
“The striations formed parallel to the direction of flow, which ultimately created subtle ridges and valleys on the top of the iceberg that now direct the flow of meltwater,” explained Walt Meier, a senior research scientist at the National Snow & Ice Data Center. “It’s impressive that these striations still show up after so much time has passed, massive amounts of snow have fallen, and a great deal of melting has occurred from below,” added retired University of Maryland Baltimore County scientist Chris Shuman.
The MODIS image suggests that the ailing iceberg has also sprung a leak. The white area to its left may be the result of what Shuman described as a “blowout.” The weight of the water pooling at the top of the towering iceberg would have created enough pressure at the edges to punch through. The blowout may have allowed meltwater to spill tens of meters down to the ocean surface in what researchers call a “freshwater discharge plume,” where it mixed with the mélange of ice bits floating next to the iceberg.
Scientists say these signs indicate the iceberg could be just days or weeks from disintegrating completely. “I certainly don’t expect A-23A to last through the austral summer,” said Shuman, noting that the season typically brings clearer skies and warmer air and water temperatures—factors that accelerate the disintegration process in an area known among ice experts as a “graveyard” for icebergs. It’s already in water that’s about 3 degrees Celsius and riding currents that are pushing it toward even warmer waters that will eat away at it quickly, added Meier.
Even by Antarctic standards, A-23A has had a long, winding journey full of unexpected chapters that have improved scientists’ understanding of the “megabergs” occasionally released into the Southern Ocean. After grounding in the shallow waters of the Weddell Sea for more than 30 years, A-23A broke free in 2020, then spent several months in a twirling ocean vortex called a Taylor column. It eventually spun away and headed north, nearly colliding with South Georgia island and lodging in shallow waters for several months before escaping into the open ocean, where it has been rapidly breaking apart throughout 2025.
Scientists who have been tracking the berg for their entire careers see its imminent demise as a bittersweet moment. “I’m incredibly grateful that we’ve had the satellite resources in place that have allowed us to track it and document its evolution so closely,” said Shuman. “A-23A faces the same fate as other Antarctic bergs, but its path has been remarkably long and eventful. It’s hard to believe it won’t be with us much longer.”
Even as A-23A fades, other massive bergs are parked or drifting along the Antarctic shoreline. Several, including A-81, B22A, and D15A, are each larger than 1,500 square kilometers and sit waiting for their moment to break free and begin their journey north.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Michala Garrison, using MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE and GIBS/Worldview. ISS Astronaut photograph ISS074-E-8943 was acquired on December 27, 2025, with a Nikon Z 9 digital camera using a focal length of 500 millimeters. It is provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations Facility and the Earth Science and Remote Sensing Unit at NASA Johnson Space Center. The image was taken by a member of the Expedition 74 crew. The image has been cropped and enhanced to improve contrast, and lens artifacts have been removed. The International Space Station Program supports the laboratory as part of the ISS National Lab to help astronauts take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth. Story by Adam Voiland.
References and Resources
- AP News (2025, September 4) Most enduring and biggest iceberg breaks apart, with more splintering to come in its death spiral. Accessed January 7, 2026.
- British Antarctic Survey (2025, March 4) World’s largest iceberg grounds near sub-Antarctic Island of South Georgia. Accessed January 7, 2026.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2025, September 24) A Giant Iceberg’s Final Drift. Accessed January 7, 2026.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2025, August 1) Antarctic Iceberg Downsizes. Accessed January 7, 2026.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2025, May 6) Antarctic Iceberg Loses Its Edge. Accessed January 7, 2026.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2015, February 6) Flipped, Dirty, Amazing Icebergs. Accessed January 7, 2026.
- NPR (2025, September 5) The world’s oldest and largest iceberg will soon be no more. Accessed January 7, 2026.
- Scambos, T., et al. (2025) How to train your iceberg: Iceberg A23a drift track in 2024. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 106(8), S357–S400.
- Scambos, T., et al. (2005) ICESat profiles of tabular iceberg margins and iceberg breakup at low latitudes. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(23).
- USA Today (2025, September 4) World’s largest iceberg, A23a, breaks. See satellite and aerial views. Accessed January 7, 2026.
- U.S. National Ice Center (2026, January 7) Antarctic Iceberg Data. Accessed January 7, 2026.
You may also be interested in:
Stay up-to-date with the latest content from NASA as we explore the universe and discover more about our home planet.

After a long, turbulent journey, Antarctic Iceberg A-23A is signaling its demise as it floats in the South Atlantic.

Iceberg A-23A continued to lose sizable pieces of ice during the 2025 austral winter, but it remained the planet’s largest…

Sea ice around the southernmost continent hit one of its lowest seasonal highs since the start of the satellite record.
The post Meltwater Turns Iceberg A-23A Blue appeared first on NASA Science.
Plants and Algae Swirl Across a South African Reservoir
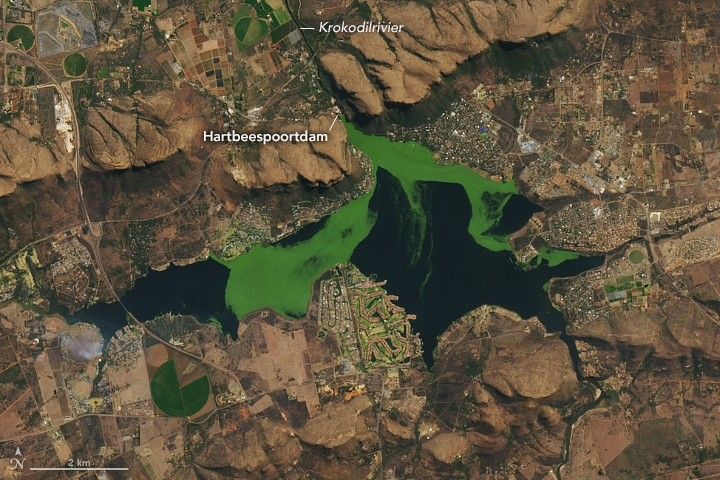
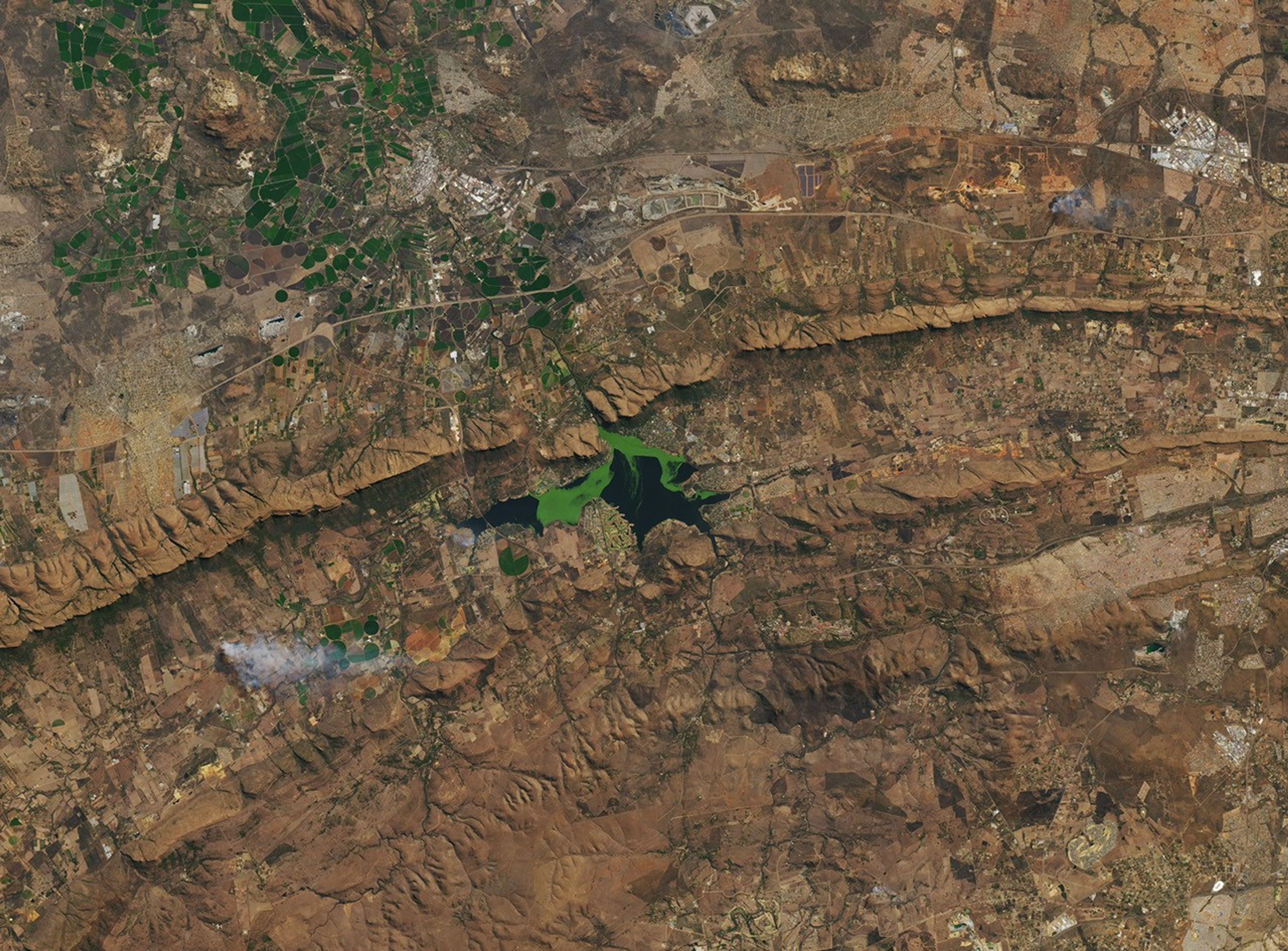
Jan. 7th, 2026 05:00 amOn clear days in Hartbeespoort, South Africa, satellite images often reveal a reservoir with shades of deep blue interrupted by drifting patches of vivid green. Over the years, these shifting features have included algae blooms—which can affect water quality, ecosystems, and nearby human communities—along with several types of invasive aquatic plants.
In this animation, from June 2022 to July 2023, aquatic plants proliferate, move around the reservoir, and then fade. The animation is composed of images from Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 (HLS), a NASA product that combines imagery from the NASA/USGS Landsat 8 and Landsat 9 satellites and the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-2A, 2B, and 2C satellites.
The green masses can also contain varying amounts of algae, an umbrella term for photosynthetic organisms that live in water, encompassing everything from single-celled cyanobacteria to seaweed. They play a vital role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. But when colonies of algae spread too widely or release harmful toxins, they can threaten the very environments they support. These colonies are known as harmful algal blooms, or HABs.
Some HABs are toxic and often are part of a process called eutrophication. Eutrophication begins when there are too many nutrients in an ecosystem—because of agricultural runoff and other inputs—leading to a rapid growth of algae.
“It’s like having a garden,” said Bridget Seegers, a NASA scientist who studies cyanobacteria in freshwater ecosystems. “If you add a lot of nutrients, you’re going to have a lot of growth.”
Eventually, the algae die off. As decomposers break down the dead algae, they consume oxygen, which can lead to hypoxia and the formation of dead zones.
Such conditions have been documented at the Hartbeespoortdam (Hartbeespoort Dam) reservoir, located about 25 kilometers (16 miles) west of Pretoria and used primarily for recreation and irrigation. It also hosts large mats of invasive water hyacinths and, more recently, the invasive plant Salvinia minima. While these aquatic plants do not produce toxins, they do contribute to eutrophication when they die and decompose.
Harmful algal blooms can affect ecosystem health and human lives and livelihoods. In April 2023, South African authorities linked a large fish kill in Hartbeespoort to low oxygen levels caused by excessive algal growth. More broadly, HABs in drinking water reservoirs can reduce water availability and raise water treatment costs, while swimming in HAB-infested waters can cause rashes, and pets or livestock that drink it may fall ill or die.
One 2022 paper published in Remote Sensing examined algae in the reservoir from 1980 to 2020 using Landsat data. “This is a reservoir that has always been monitored heavily by the local department of water resources,” said Adam Ali, the lead author of the paper. The research used satellite data to provide a big-picture view of conditions across the entire reservoir over long time scales. Using 40 years of Landsat data, the researchers found that the biggest drivers of algal growth were total phosphorus content—a nutrient found in runoff—and water temperature, with blooms typically expanding in the warm summer months and subsiding in the winter.
They also identified key trends over space and time. Algal productivity was higher near Krokodilrivier (Crocodile River) inflows and in the western part of the reservoir due to golf course runoff and restricted water circulation, demonstrating how HABs are influenced by runoff and river inputs. Large blooms occurred between 1982 and 1986, when total phosphorus levels were high. A bioremediation program in the late 1980s succeeded in limiting algae growth, but after funding ended in the late 1990s, harmful algal blooms spiked again in the early 2000s.
To track algae from space, the researchers analyzed the water’s color by measuring different wavelengths of light. From this, they estimated the concentration of chlorophyll-a, a common pigment in algae, and used these values to approximate algae biomass over time. Although water samples remain necessary to confirm that a bloom is harmful, satellite data can help scientists understand the drivers of harmful algal blooms, especially in remote regions where regular ground monitoring is expensive and time intensive.
New and forthcoming NASA missions promise to advance space-based water quality monitoring. The next Landsat satellite is expected to measure wavelengths specifically designed to detect HABs. NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) mission, launched in 2024, collects data in hundreds of precise wavelength bands in the visible spectrum, which can help scientists identify the type of algae that comprise a certain bloom—a key factor in determining toxicity. Given PACE’s spatial resolution, the data is most useful in coastal areas or larger inland water bodies. Ali is working with researchers at NASA Ames to integrate PACE into future studies.
Editor’s note: This story was updated on January 13, 2026, to note the presence of the plant Salvinia minima.
Animation by Ross Walter/Landsat Science Office Support, using data from the Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 (HLS) product. HLS is funded by NASA and is a deliverable of the Satellite Needs Working Group (SNWG), an interagency effort of the U.S. Government dedicated to identifying and addressing Earth observation needs across U.S. civilian federal agencies. Still image by Lauren Dauphin/NASA Earth Observatory using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey. Story by Madeleine Gregory/Landsat Science Office Support.
References & Resources
- Ali, K., et al. (2022) Integrating In Situ and Current Generation Satellite Data for Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Harmful Algal Blooms in the Hartbeespoort Dam, Crocodile River Basin, South Africa. Remote Sensing, 14(17), 4277.
- Coetzee, J.A., et al. (2022) Into Africa: Salvinia minima Baker (Salviniaceae) invades South Africa. BioInvasions Records, 11(14), 1011-1018.
- NOAA (2016, April 27) What is a harmful algal bloom? Accessed January 6, 2026.
- South African Government (2023, April 26) Water and Sanitation releases investigation report on cause of fish-kill at Hartbeespoort Dam. Accessed January 6, 2026.
You may also be interested in:
Stay up-to-date with the latest content from NASA as we explore the universe and discover more about our home planet.

A multi-year drought has put extra strain on farmers and water managers in the Middle Eastern country.

Drought in the Nueces River basin is reducing reservoir levels, leaving residents and industry in the Corpus Christi area facing…

Forests play a key role in filtering the waters of a reservoir in central Massachusetts that’s home to submerged towns…
The post Plants and Algae Swirl Across a South African Reservoir appeared first on NASA Science.
In southwestern Angola, an expanse of coastal plains comes to an abrupt end at a natural barrier. The Huíla plateau soars above the lowlands to elevations of around 2,300 meters (7,500 feet). The sharp transition results in dramatic landscapes and a sudden change from an arid environment to more-temperate climes.
The serrated edge of the Huíla plateau zigzags through this image, which is a mosaic of scenes acquired on June 19 and 20, 2025, with the OLI-2 (Operational Land Imager-2) and OLI on the Landsat 9 and Landsat 8 satellites, respectively. Areas around the plateau’s edges appear green with vegetation. But the landscape tends to look much browner by late September, at the end of the region’s dry season, during which almost no rain falls.
This topography is part of the Great Escarpment of southern Africa, a 5,000-kilometer-long feature running roughly parallel to the continent’s edge. From Angola, it extends south through Namibia, across South Africa, and then northeast into Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The image below, acquired with the VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) on the Suomi NPP satellite, shows a longer segment of the escarpment in Angola.
Scientists believe the escarpment formed after the breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana in the Jurassic period. Since then, erosion has worn away at the continental margin such that the escarpment now sits 50 to 200 kilometers (30 to 120 miles) back from the coast.
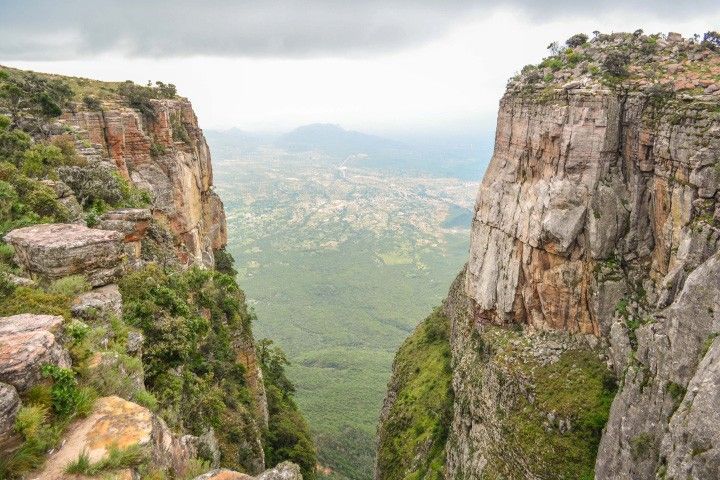
This Angolan section of the escarpment features dizzying, yet beautiful, landscapes. Tundavala Gap, a gouge eroded into the cliff line (below), is one of the most iconic with its well-framed view of the plains below. The precipice also presents a substantial obstacle to transportation. A stretch of the Namibe-Lubango Road overcomes this challenge with a series of scenic hairpin turns climbing to Serra da Leba pass near the town of Leba.
Lubango, one of Angola’s largest cities, occupies a valley on the Huíla plateau. In addition to its remarkable natural surroundings, the city boasts a diverse mix of cultures, striking architecture, and a wide variety of locally produced foods.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Wanmei Liang, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey, and VIIRS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE, GIBS/Worldview, the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership, and the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS). Photo of Tundavala Gap © jbdodane.com. Story by Lindsey Doermann.
References & Resources
- African Leadership Magazine (2024, May 3) Unveiling Lubango, the Hidden Gem of Southern Angola. Accessed January 5, 2026.
- The American Alpine Journal (2024) Fenda da Tundavala and Serra da Leba, New Routes. Accessed January 5, 2026.
- Atlas Obscura (2025, August 18) Serra da Leba Pass. Accessed January 5, 2026.
- Clark, V.R., et al. (2011) The Great Escarpment of southern Africa: a new frontier for biodiversity exploration. Biodiversity and Conservation, 20, 2543–2561.
- CNN (2023, November 27) Lubango: The spectacular African destination you’ve probably never heard of. Accessed January 5, 2026.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2017, March 13) South Africa’s “Brown Gold.” Accessed January 5, 2026.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2013, December 14) South Africa Tribute. Accessed January 5, 2026.
You may also be interested in:
Stay up-to-date with the latest content from NASA as we explore the universe and discover more about our home planet.

Researchers are using satellites to study development patterns in this fast-growing city in Ethiopia.

Satellites are helping land managers track ecological shifts as reserves reconnect and landscapes return to a more natural state.

Satellites have tracked development over the decades as a small city in southern Nigeria grew to more than 2 million…
The post Reaching the Precipice in Angola appeared first on NASA Science.